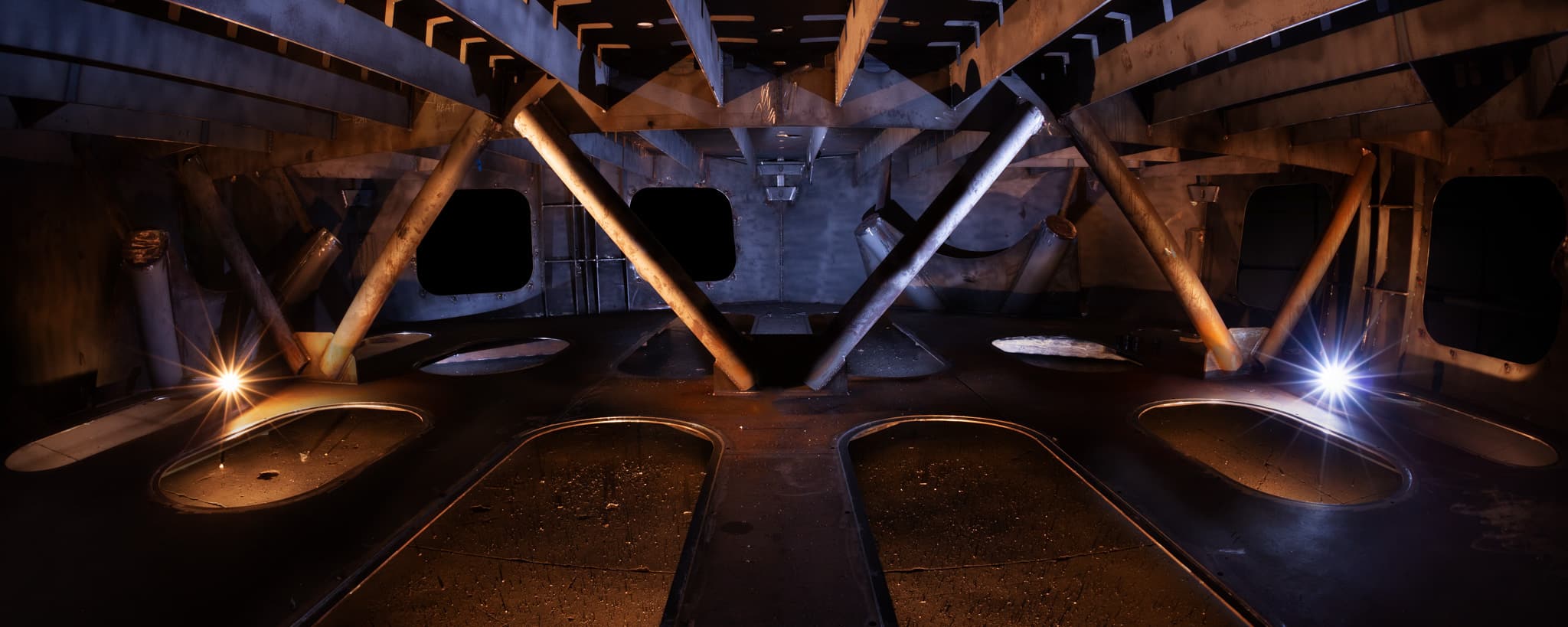
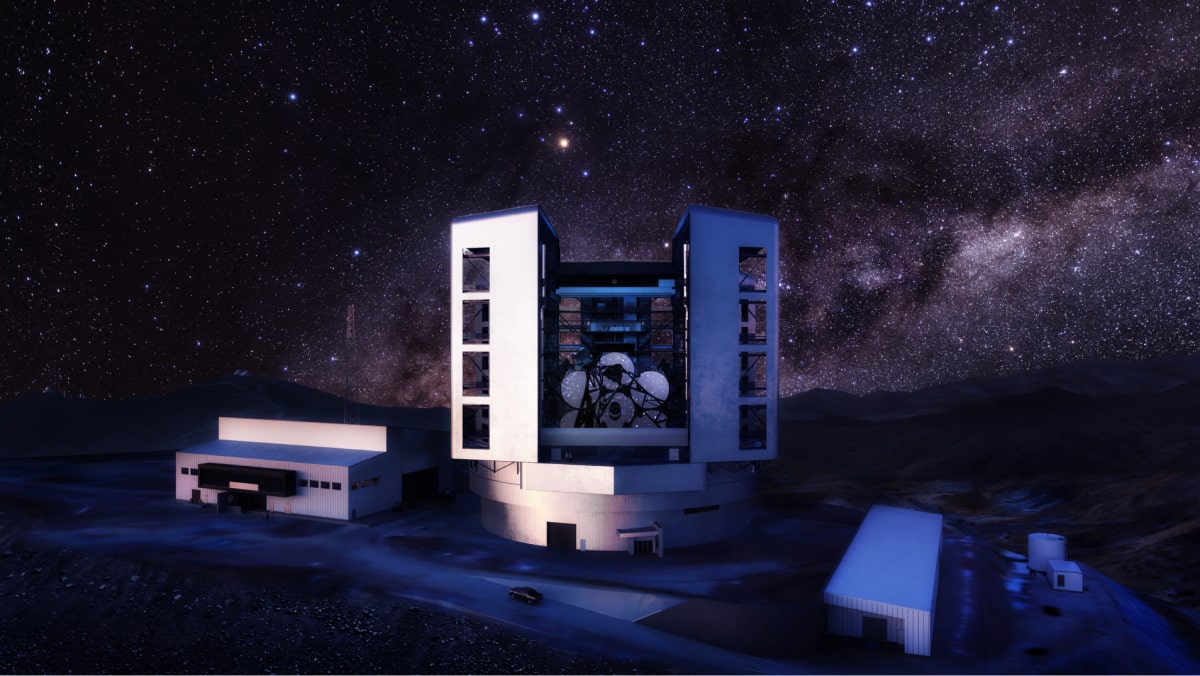
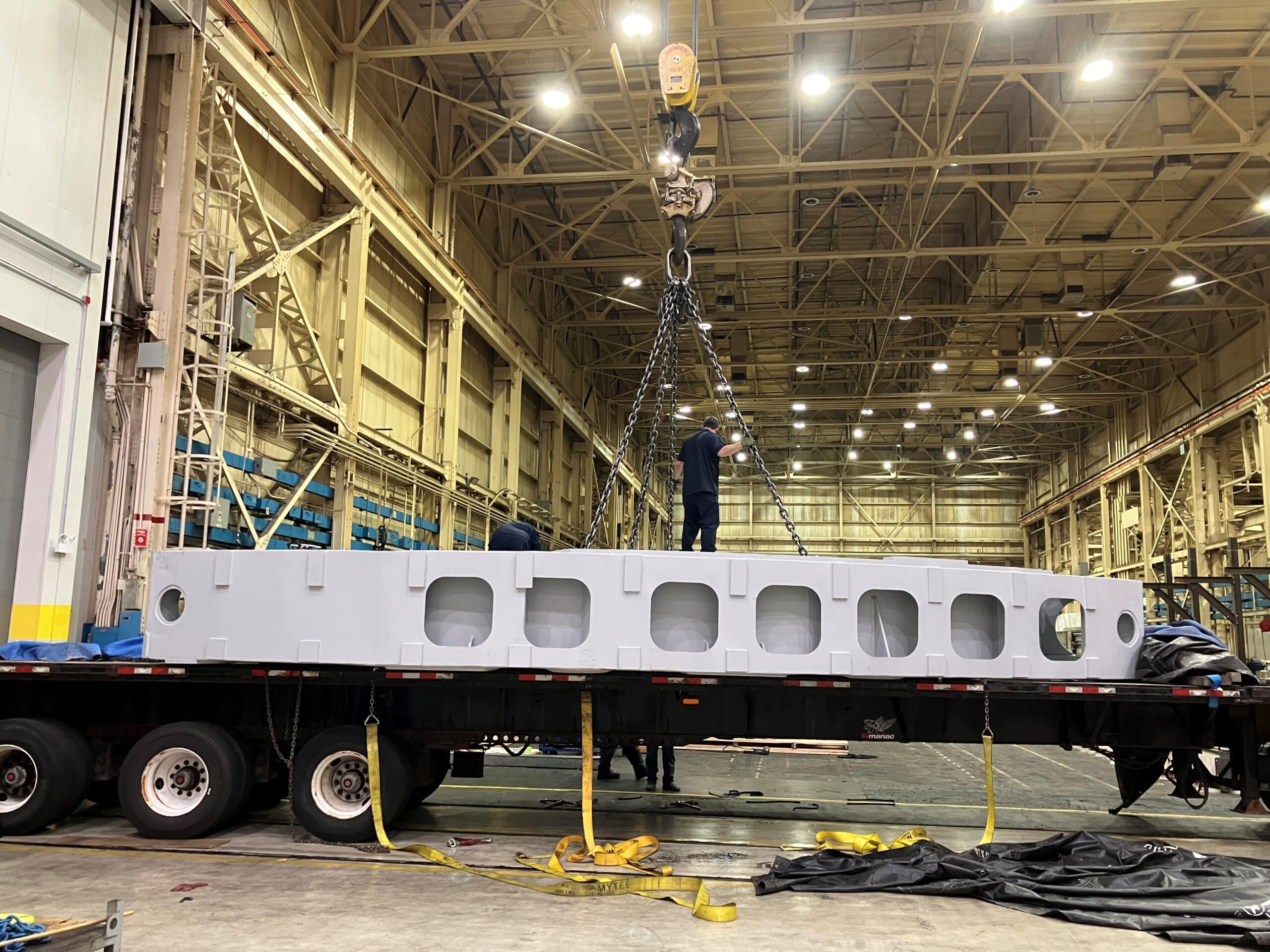
Telescope Mount
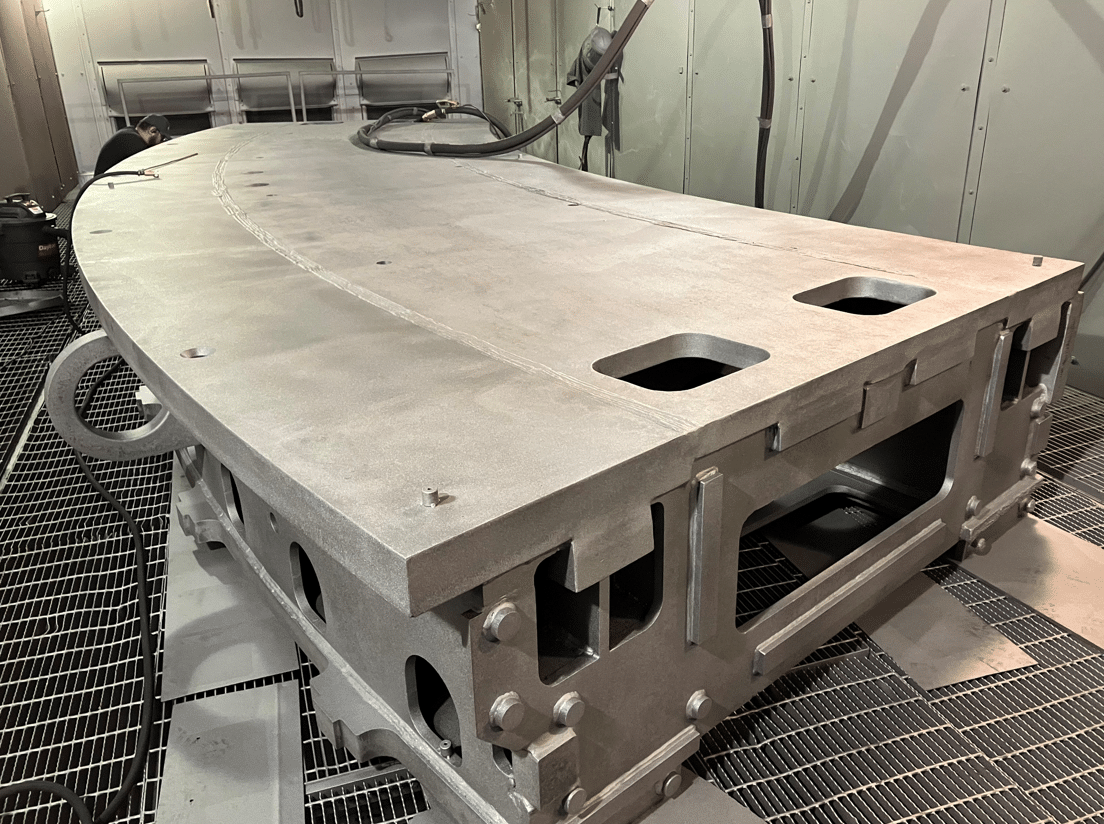
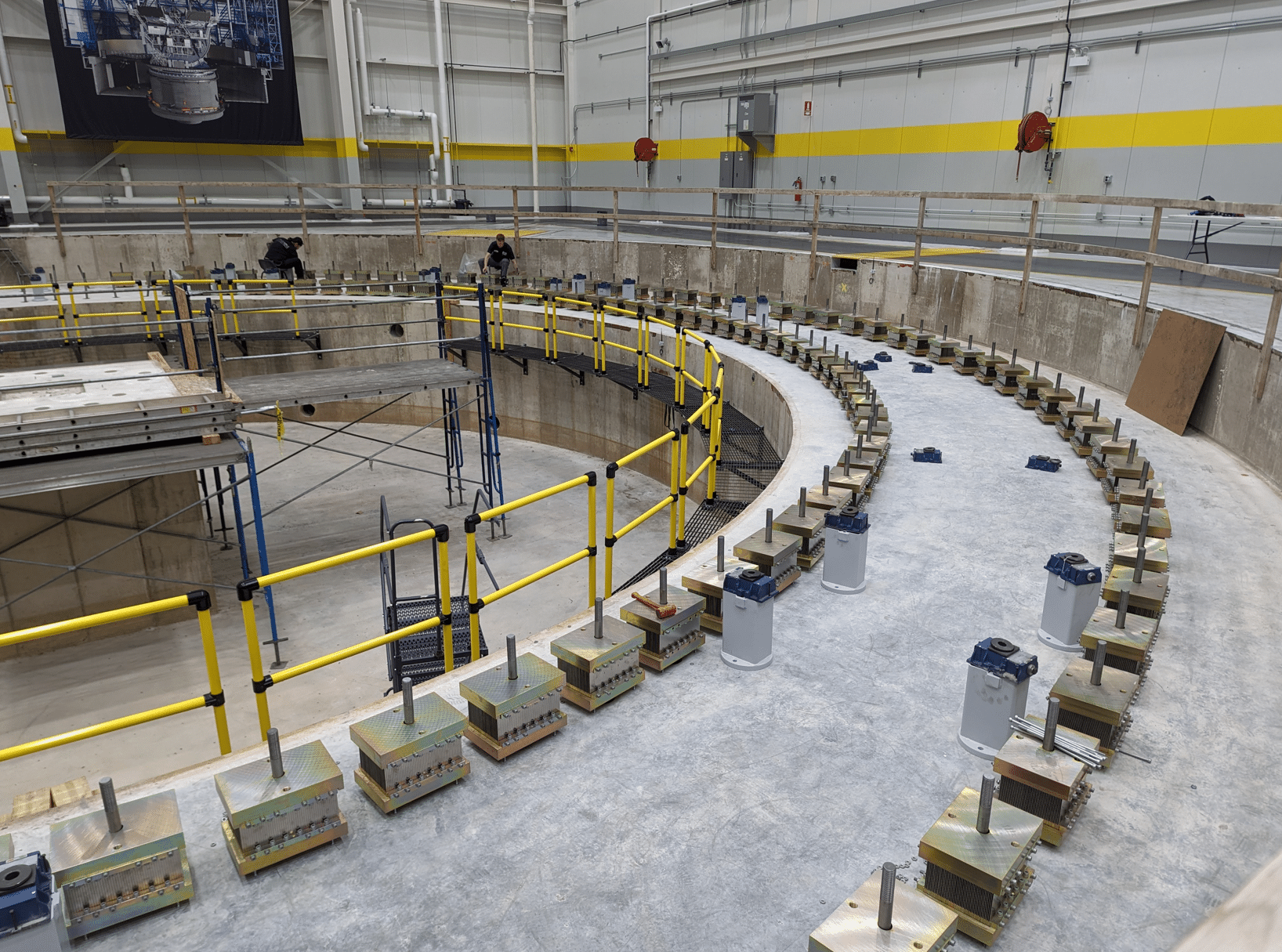
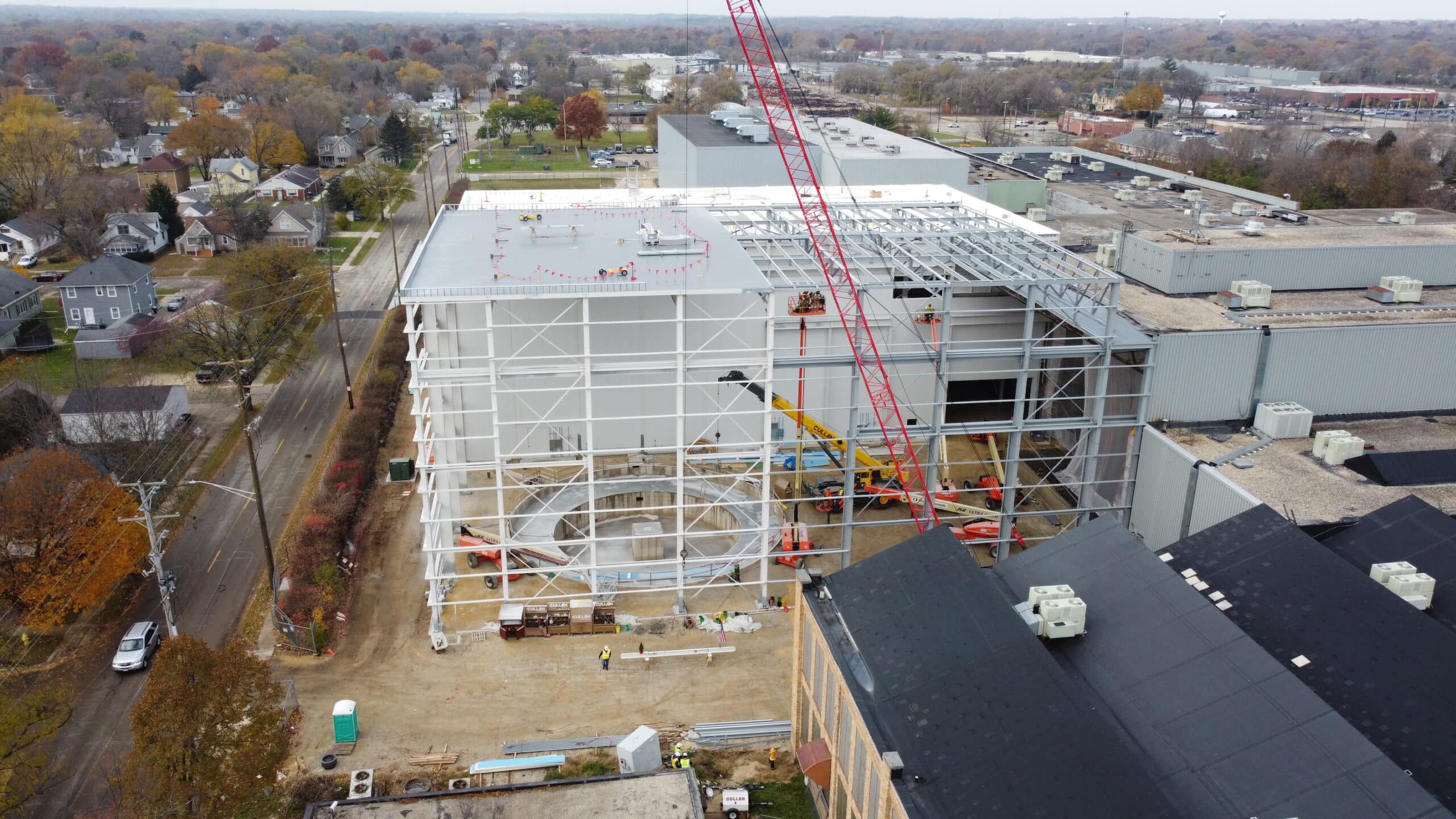
The Giant Magellan Telescope mount provides the supporting framework for the world’s largest mirrors, adaptive optics, scientific instruments, and control systems. The 39-meter-tall structure is being developed in Arizona and Illinois.
Copyright of the GMTO Corporation. Unless otherwise noted, credit with: “Giant Magellan Telescope – GMTO Corporation." To receive permission for non-commercial or commercial use, email info@gmto.org.
Select type
Images
Videos
Select Topic
Select Year
reset all


 5 /
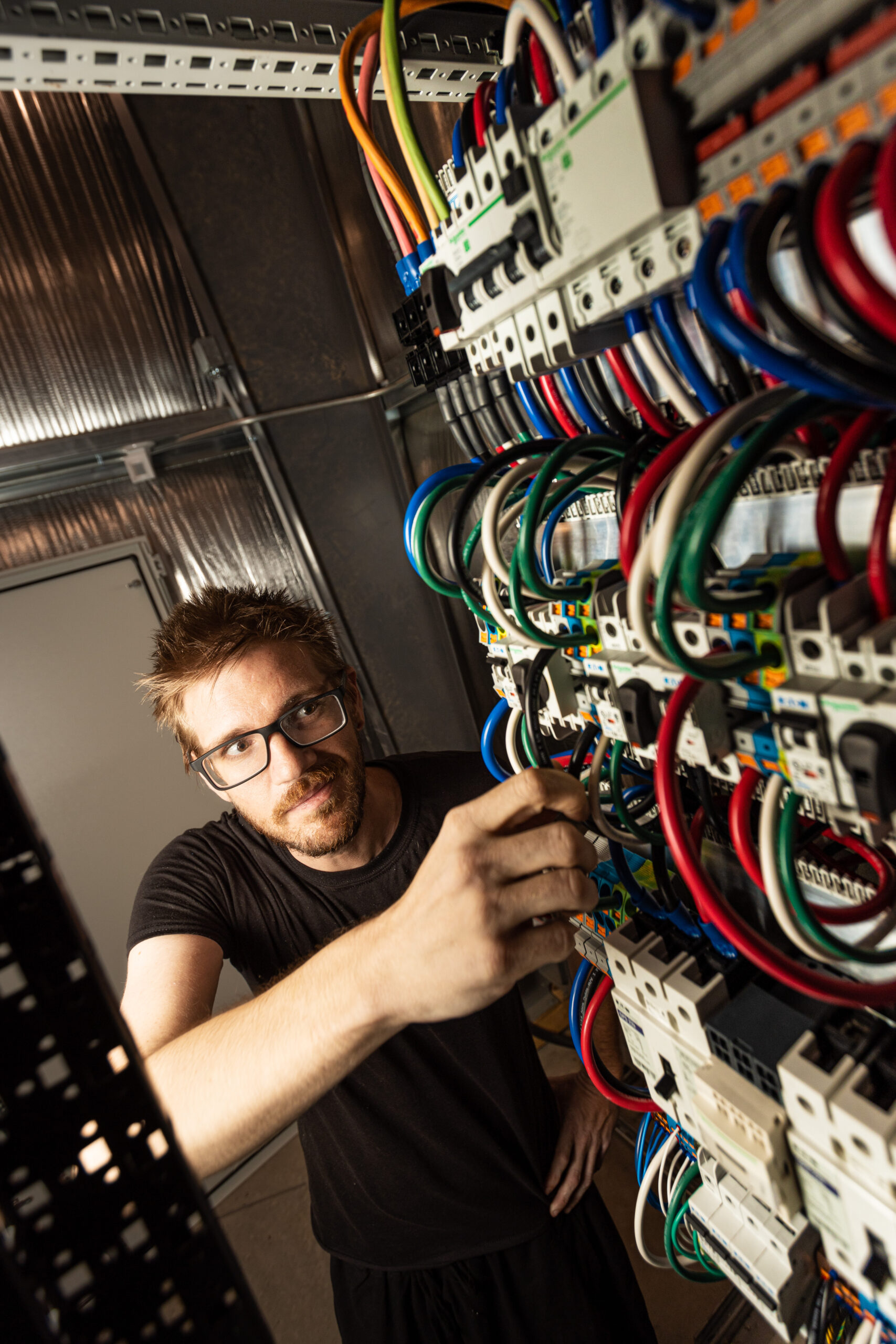
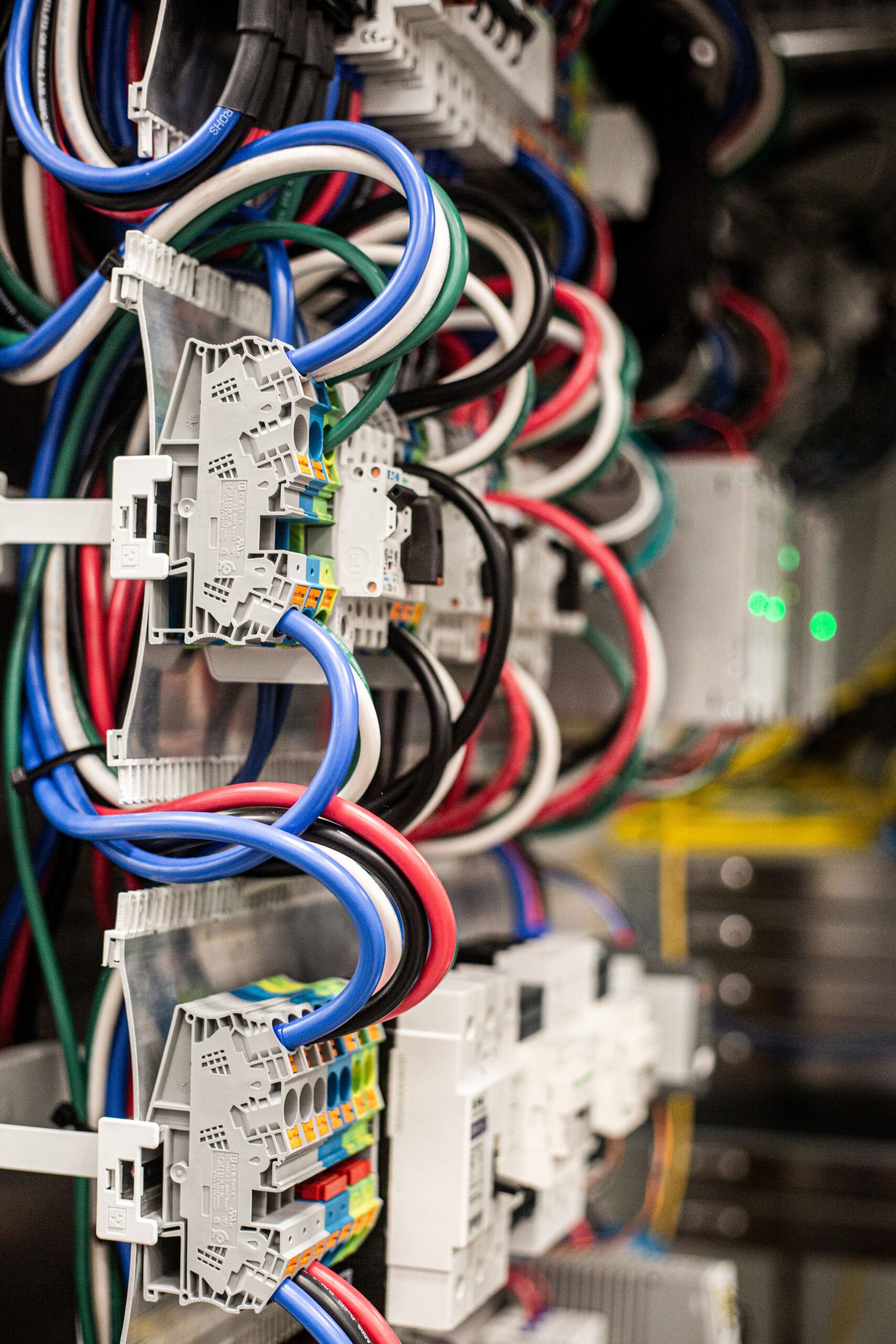
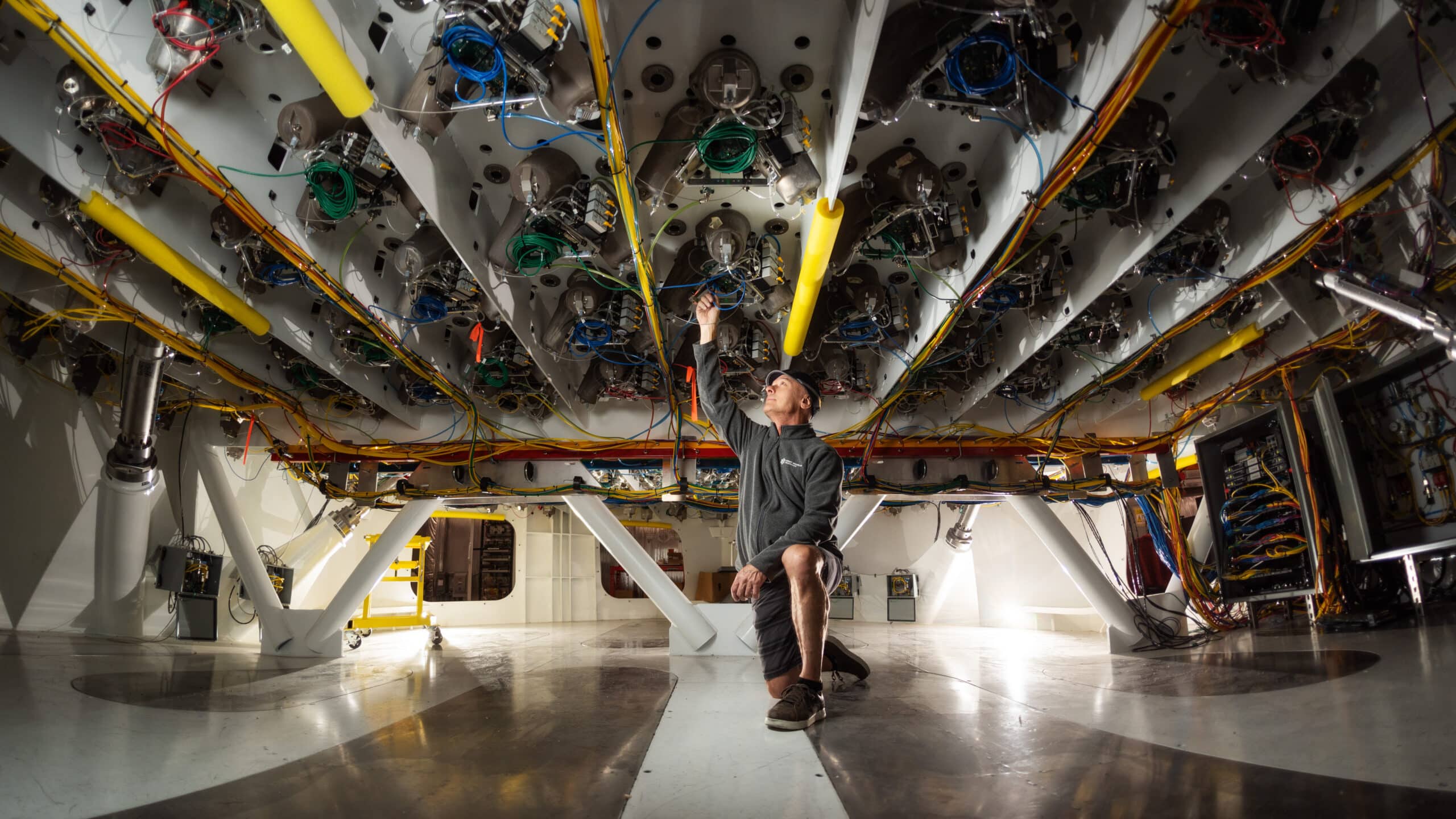
Electronic Bench Technician Austin Everman checking wires inside server cabinets at the University of Arizona Tech Park. Image credit: Damien Jemison, Giant Magellan Telescope – GMTO Corporation
5 /
Electronic Bench Technician Austin Everman checking wires inside server cabinets at the University of Arizona Tech Park. Image credit: Damien Jemison, Giant Magellan Telescope – GMTO Corporation




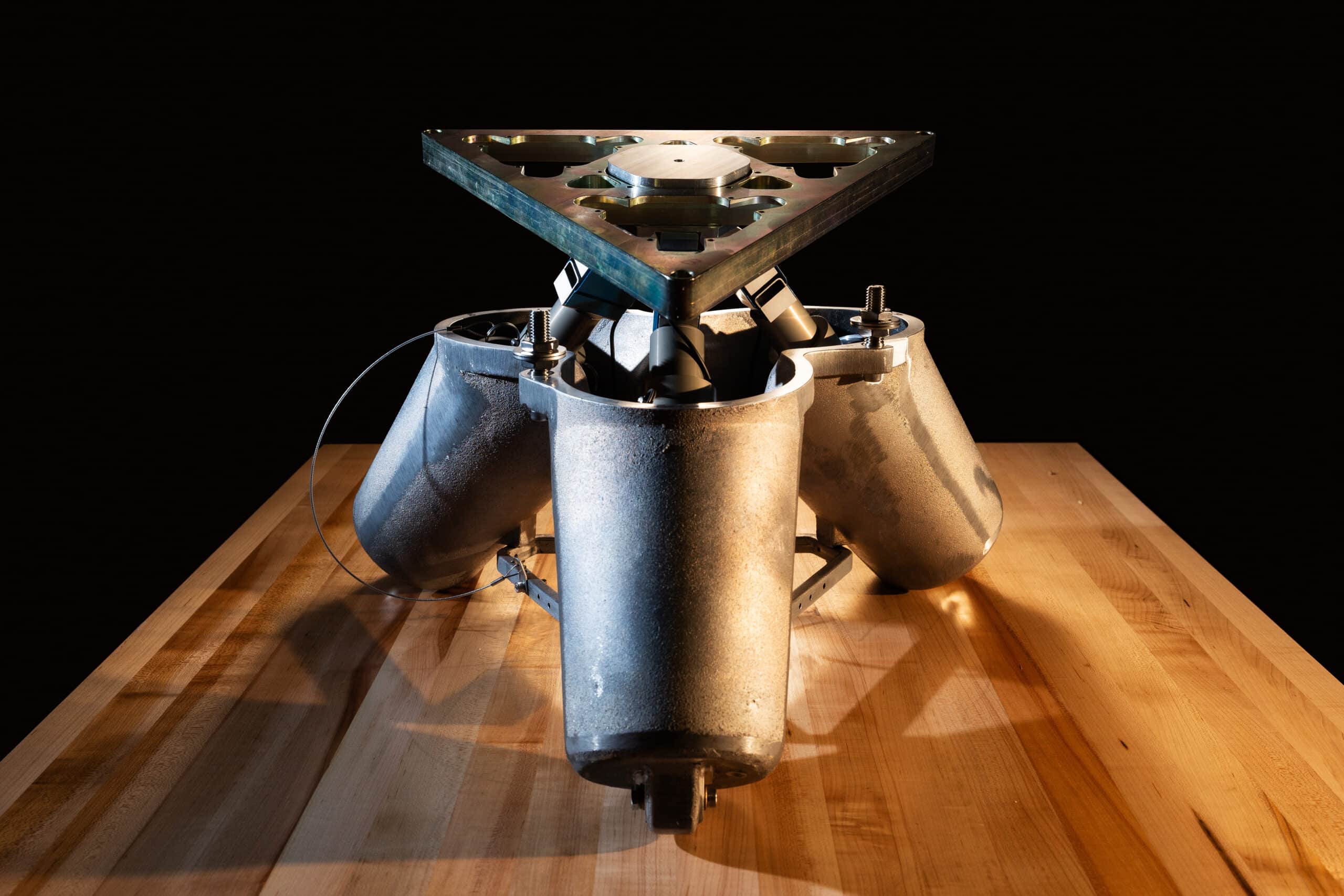
 12 /
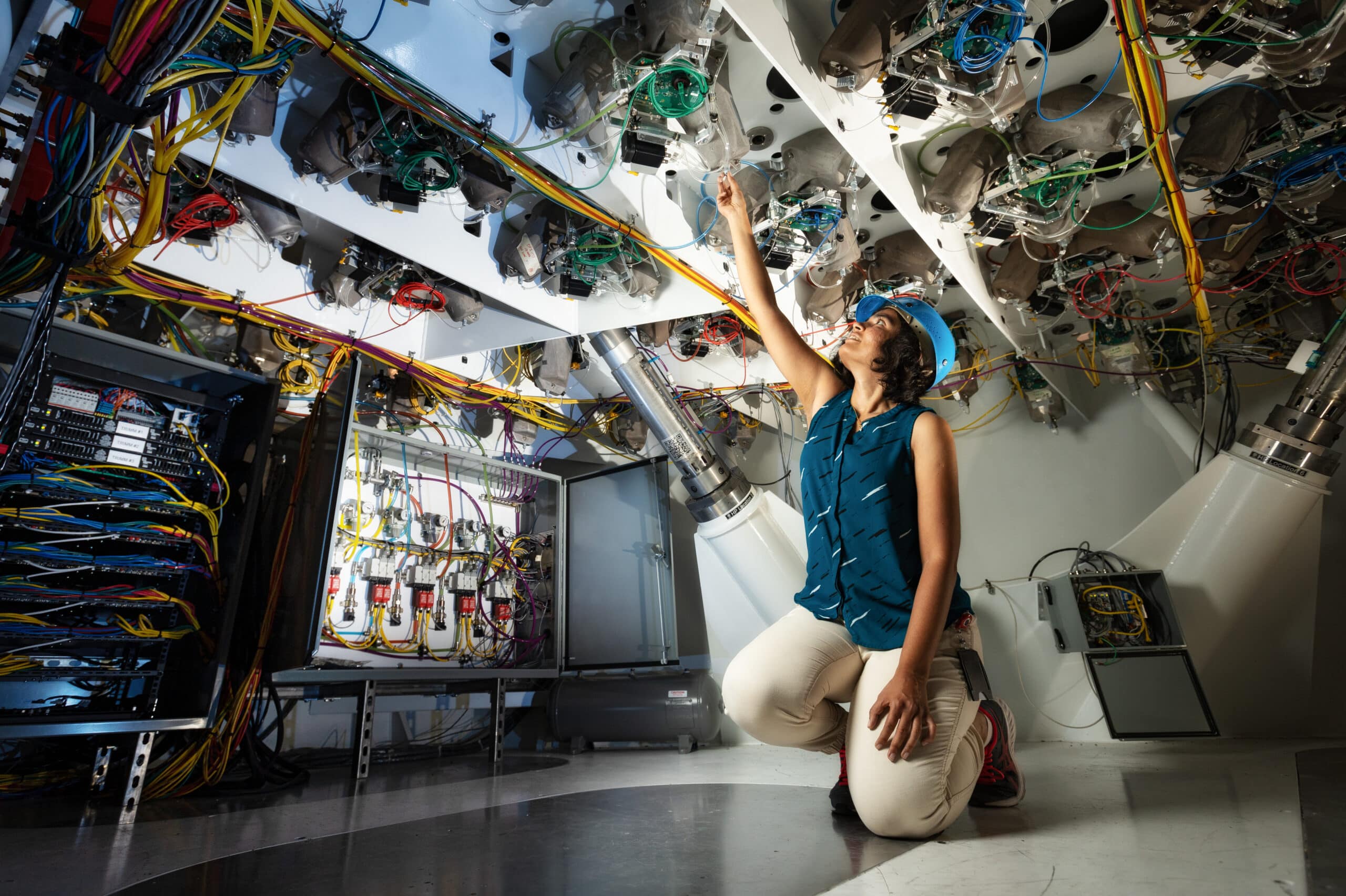
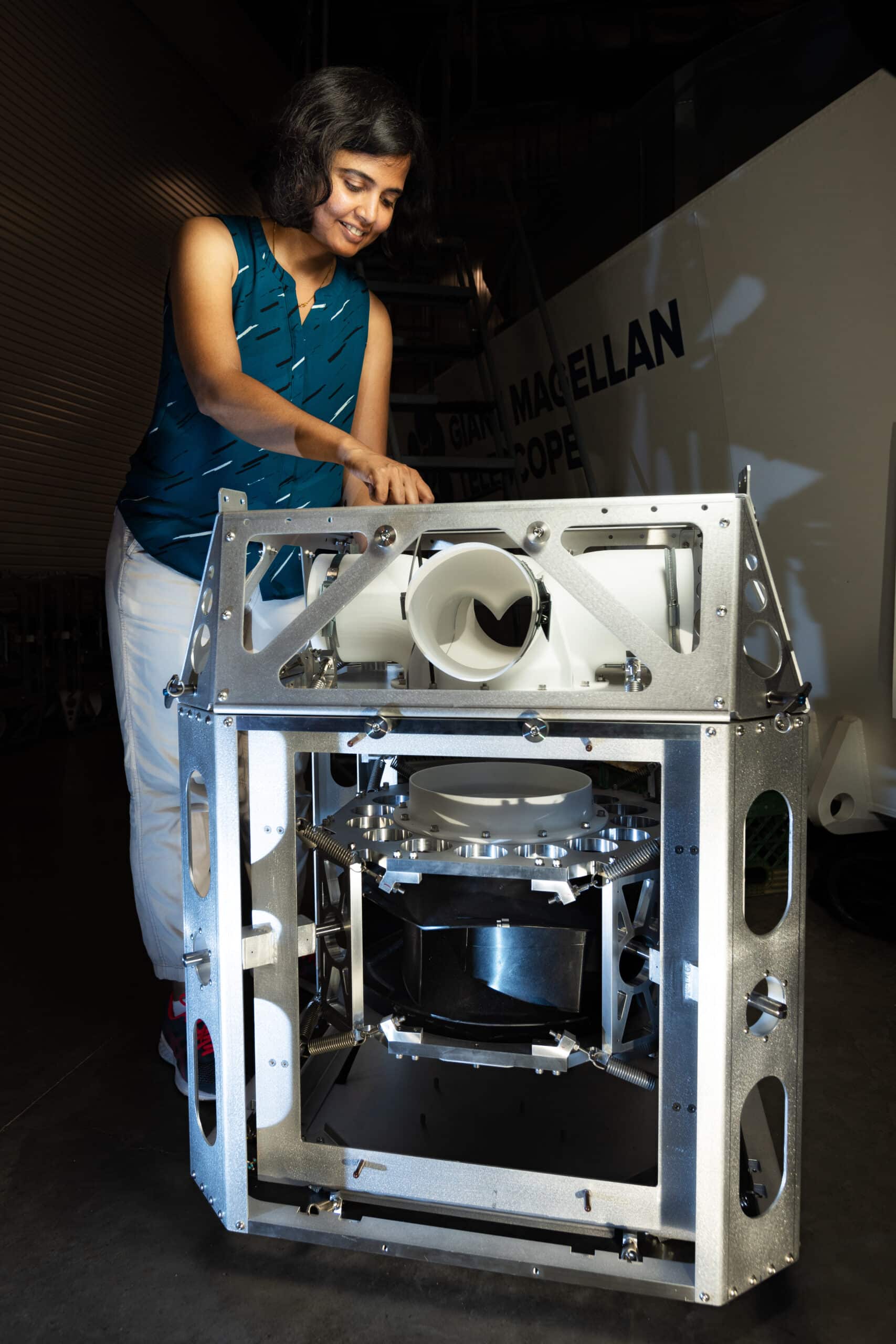
Primary mirror support system prototype at the University of Arizona Tech Park. Senior Control Systems Engineer Trupti Ranka is shown (right) running testing on the prototype. Image credit: Damien Jemison, Giant Magellan Telescope – GMTO Corporation
12 /
Primary mirror support system prototype at the University of Arizona Tech Park. Senior Control Systems Engineer Trupti Ranka is shown (right) running testing on the prototype. Image credit: Damien Jemison, Giant Magellan Telescope – GMTO Corporation

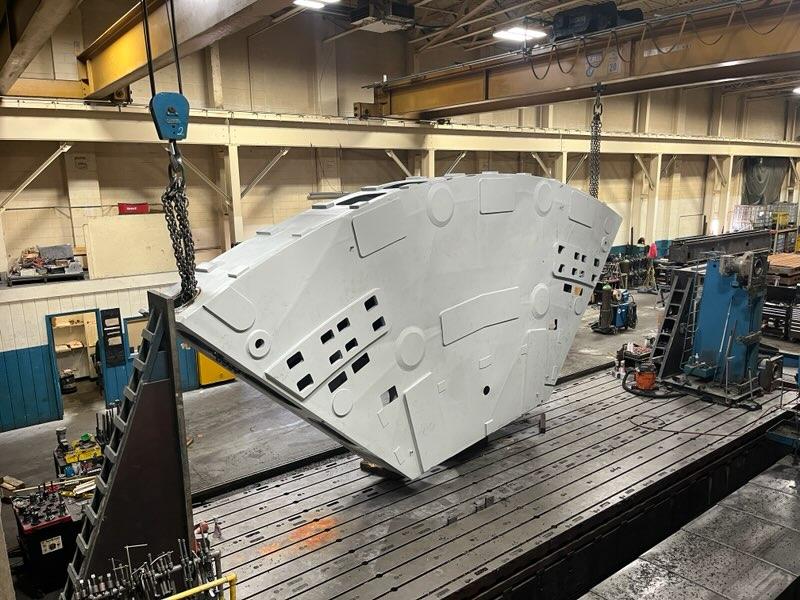
 15 /
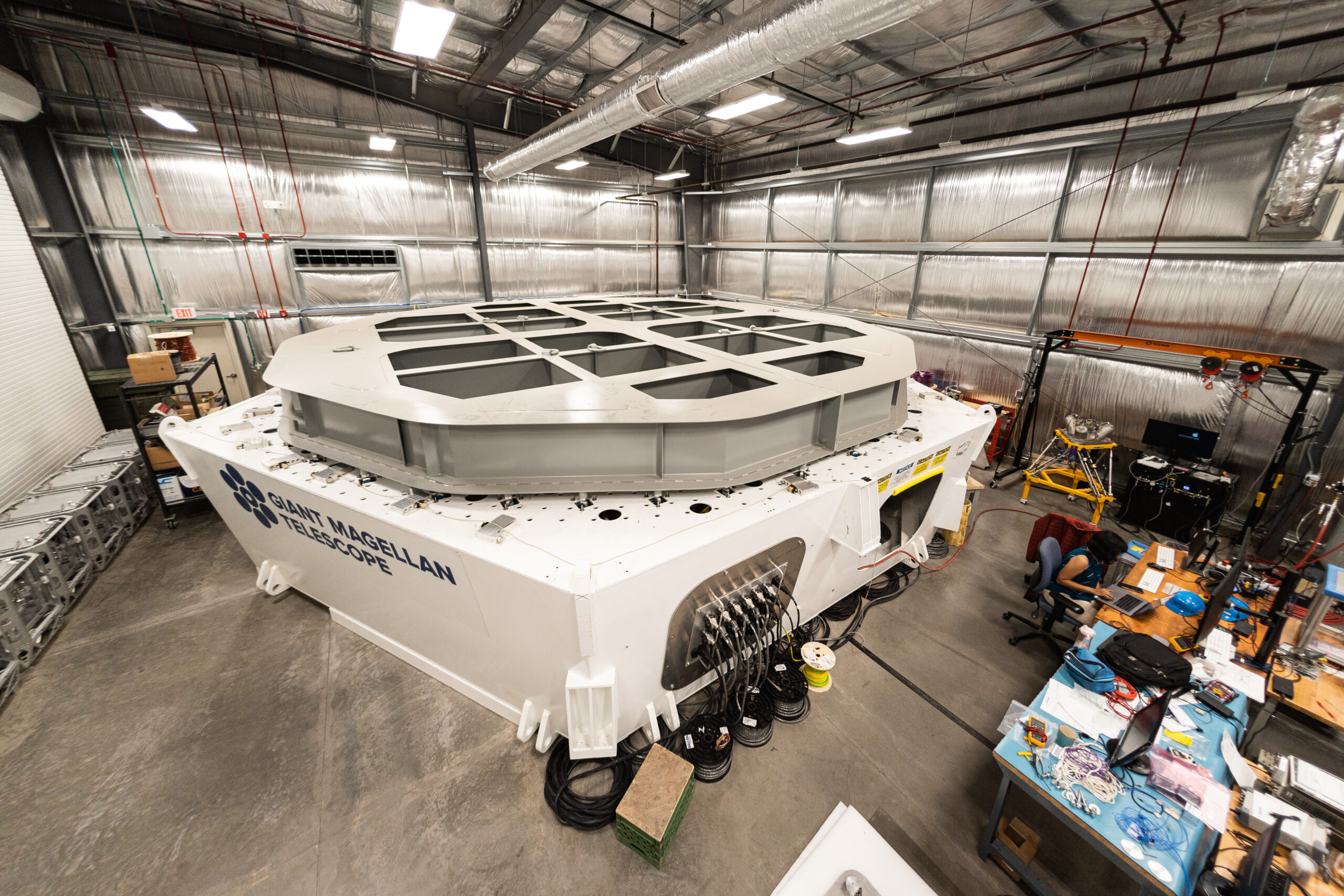
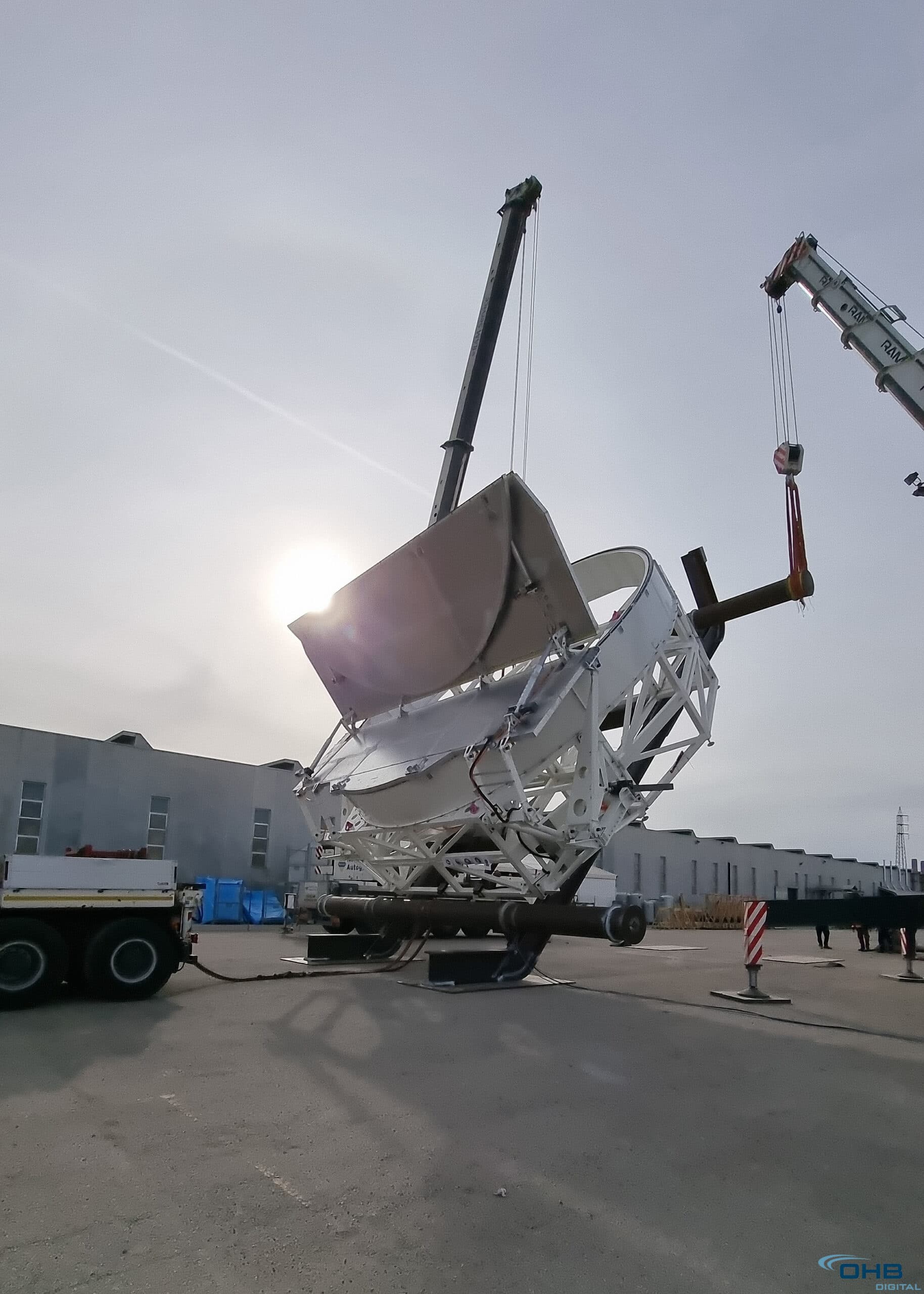
First of seven mirror covers for the telescope. In just over two minutes, the covers will deploy and retract in unison to protect the mirrors when they’re not in use. Image credit: OHB Italia SpA
15 /
First of seven mirror covers for the telescope. In just over two minutes, the covers will deploy and retract in unison to protect the mirrors when they’re not in use. Image credit: OHB Italia SpA

